Urban Morphological Feature Extraction and Multi-Dimensional Similarity Analysis Based on Deep Learning Approaches
Abstract
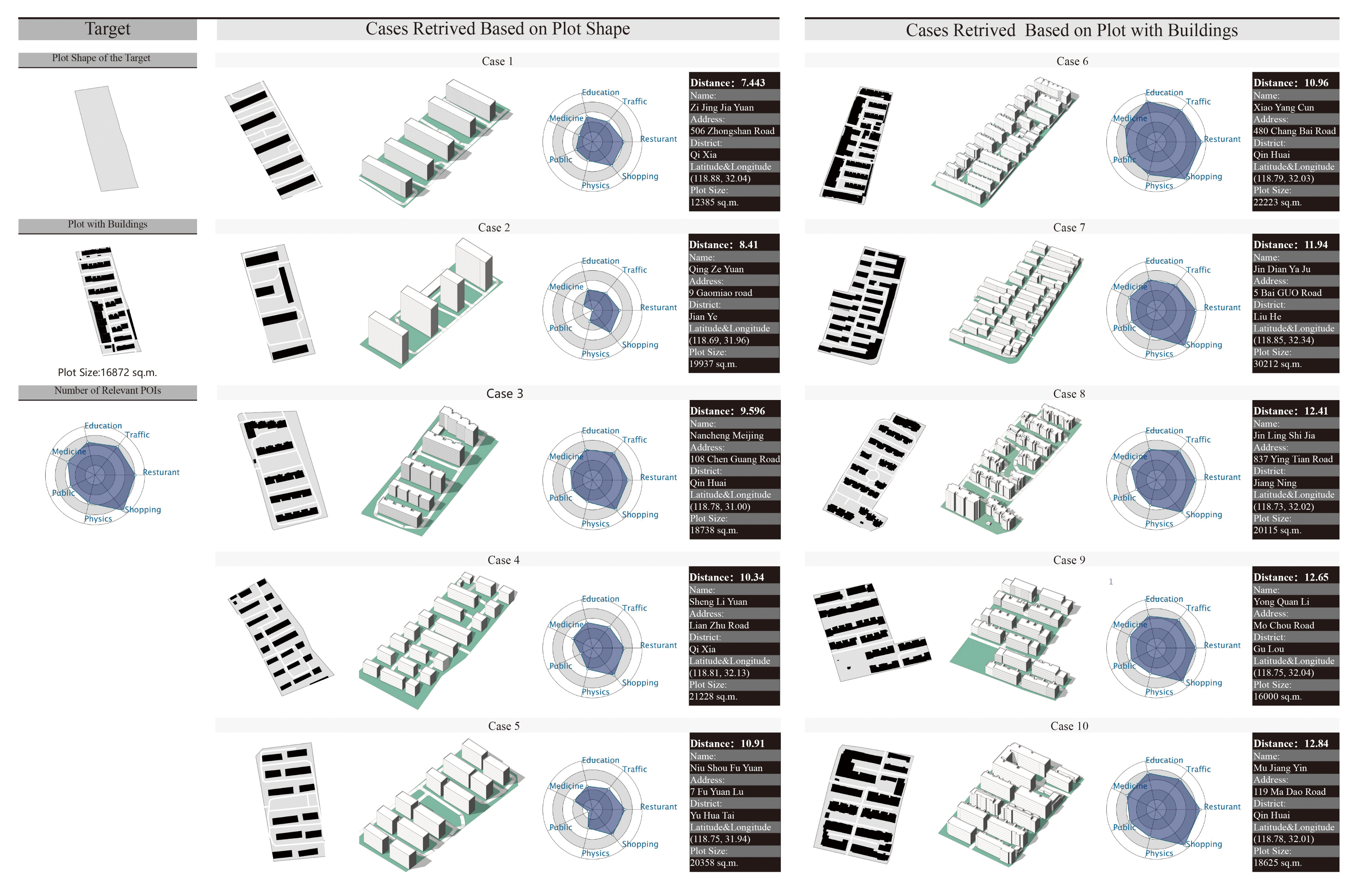
The study of urban morphology contributes to the evolution of cities and sustainable development. Urban morphological feature extraction and similarity analysis represents a practical framework in many studies to interpret and introduce the current built environment to aid in proposing novel designs. In conventional methods, morphological features are represented based on qualitative descriptions, symbolical interpretation, or manually selected indicators. However, these methods could cause subjective bias and limit the generalizability. This study proposes a hybrid data-driven approach to support quantitative morphological descriptions and multi-dimensional similarity analysis for urban design decision-making and to further morphology-related studies using information abundance via a deep-learning approach. We constructed a dataset of 3817 residential plots with geometrical and related infrastructure information. A deep convolutional neural network, GoogLeNet, was implemented with the plots’ figure–ground images, by quantifying the morphological features into 2048-dimensional feature vectors. We conducted a similarity analysis of the plots by calculating the Euclidean distance between the high-dimensional feature vectors. Then, a comparison study was performed by retrieving cases based on the plot shape and plots with buildings separately. The proposed method considers the overall characteristics of the urban morphology and social infrastructure situations for similarity analysis. This method is flexible and effective. The proposed framework indicates the feasibility and potential of integrating task-oriented information to introduce custom and adequate references via deep learning methods, which could support decision making and association studies on morphology with urban consequences. This work could serve as a basis for further typo-morphology studies and other morphology-related ecological, social, and economic studies for sustainable built environments.
Keywords
urban morphology; deep learning; similarity analysis; cluster analysis; feature extraction